ATR’s ETOPS 120 Certification Renewed: What it Means for Regional Connectivity
The European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) renewed the ETOPS 120 certification for the ATR 72-600 for another two years. This renewal is an endorsement of ATR’s commitment to safe, efficient and flexible regional air travel.

What is ETOPS and Why It Matters
ETOPS stands for Extended-range Twin-engine Operational Performance Standards. In simple terms, it defines how far a twin-engine aircraft can fly from the nearest suitable airport in case of an engine failure. Without ETOPS, aircraft must stay within 60 minutes of a diversion airport. With ETOPS 120, this radius doubles, extending operational flexibility.
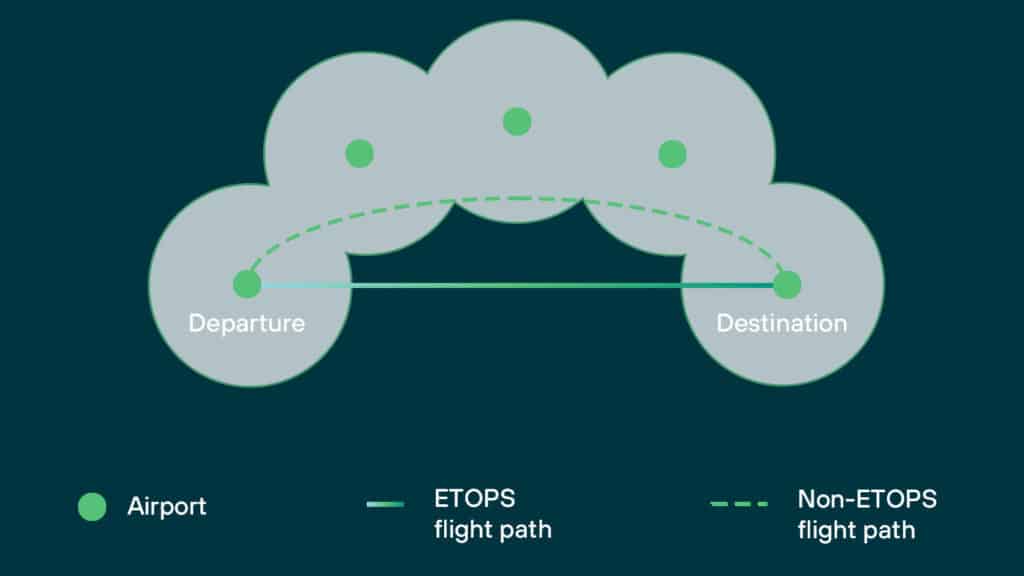
Maintaining ETOPS approval requires demonstrated system reliability typically focused on engines, fuel, fire detection, electrical, pressurization, nav/comm systems, and more, giving operators more operational freedom.
As ATR aircraft are designed for regional operations, often serving areas with limited infrastructure and few alternate airports, ETOPS 120 certification allows ATR operators to fly longer, more efficient routes.
- More direct routes between remote destinations
- Shorter flight times and lower fuel burn
- Greater flexibility in planning networks across oceans, mountains, or sparsely populated regions
And it’s not a one-time deal. ETOPS compliance must be re-demonstrated every two years.
ATR and ETOPS: A Proven Track Record
ATR submitted its first ETOPS request back in 1997 for the ATR 72-600 (certified under the ATR 72-212A designation) equipped with Pratt & Whitney PW127F engines. Certification for ETOPS 120 minutes followed in 2000 after demonstrating exceptional in-service reliability.













